Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Arai, Taiki*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Motohashi, Mitsuya*
Zairyo No Kagaku To Kogaku, 60(5), p.153 - 158, 2023/10
Si oxide films are currently widely used as insulating materials in electronic devices and biomaterials. The atomic bonding state of these films significantly influences the properties of each device, thus it is particularly necessary to understand and control the chemical bonding state between Si and O in the films. In this study, the Si oxide films formed by anodic oxidation on Si substrate surfaces in extremely low concentrations of HF solutions were analyzed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy mainly focusing on Si2p and F1s spectra. Although the HF concentration is in the order of ppm, the films contain percent order of F atoms, suggesting the formation of Si-F and Si-O-F bonds in the films. It was also found that the different depth profiles for F and O atoms was observed, indicating that the surface reaction processes seem to be different depending on each element.
Takayama, Yusuke; Yamamoto, Yoichi*; Goto, Takahiro*
Jiban Kogaku Janaru (Internet), 18(3), p.317 - 330, 2023/09
It has been reported that the deformation greatly increased in the secondary consolidation process in the past long-term consolidation test of 1.8 years on Na-type bentonite/sand mixed soil. Therefore, we analyzed potential contributing factors in this behavior. A long-term consolidation test for about 10 years on bentonite and kaolinite was started using the test equipment with countermeasures against these factors. In this paper, the secondary consolidation behavior of bentonite was investigated based on the long-term consolidation test data for 2.7, 3.7 and 4 years. The results were generally consistent with the conventional findings on soil mechanics that the deformation due to secondary consolidation progresses linearly with respect to logarithm of time. This test will be continued for about 10 years and longer-term secondary consolidation behavior will be investigated.
Nakamura, Takafumi*; Yamamoto, Yukio*; Arakawa, Masakazu*; Maruyama, Akio*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka
Sangyo Oyo Kogakukai Rombunshi, 11(2), p.109 - 114, 2023/09
Surface chemistry experimental end-station at BL23SU in SPring-8 is widely used to study various surfaces and interfaces of functional materials by means of soft X-rays synchrotron radiation. To analyze surface chemical reactions between gas and solid surfaces, an accurate control of flow-rates of gases is essential. This paper describes a computerized automatic gas flow control system to improve the accuracy and reproducibility of gas-surface reaction experiments in the pressure range of ultra-high vacuum (molecular flow) conditions. The system uses feedback control to operate the slow-leak valve to control the gas-pressure. As a result, the system achieved results equivalent to those of a skilled experimenter.
Doda, Norihiro; Nakamine, Yoshiaki*; Kuwagaki, Kazuki; Hamase, Erina; Kikuchi, Norihiro; Yoshimura, Kazuo; Matsushita, Kentaro; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 28, 5 Pages, 2023/05
As a part of the development of the "Advanced Reactor Knowledge- and AI-aided Design Integration Approach through the whole plant lifecycle (ARKADIA)" to automatically optimize the life cycle of innovative nuclear reactors including fast reactors, ARKADIA-design is being developed to support the optimization of fast reactor in the conceptual design stage. ARKADIA-Design consists of three systems (Virtual plant Life System (VLS), Evaluation assistance and Application System (EAS), and Knowledge Management System (KMS)). A design optimization framework controls the connection between the three systems through the interfaces in each system. This paper reports on the development of an optimization analysis control function that performs design optimization analysis combining plant behavior analysis by VLS and optimization study by EAS.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Asahi, Yuichi; Inagaki, Atsushi*; Shimose, Kenichi*; Hirano, Kohin*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 28, 4 Pages, 2023/05
We have developed a multi-scale wind simulation code named CityLBM that can resolve entire cities to detailed streets. CityLBM enables a real time ensemble simulation for several km square area by applying the locally mesh-refined lattice Boltzmann method on GPU supercomputers. On the other hand, real-world wind simulations contain complex boundary conditions that cannot be modeled, so data assimilation techniques are needed to reflect observed data in the simulation. This study proposes an optimization method for ground surface temperature bias based on an ensemble Kalman filter to reproduce wind conditions within urban city blocks. As a verification of CityLBM, an Observing System Simulation Experiment (OSSE) is conducted for the central Tokyo area to estimate boundary conditions from observed near-surface temperature values.
Kobayashi, Kensuke*; Yasue, Ayumu*; Morooka, Satoshi; Kanematsu, Manabu*
Konkurito Kogaku Nenji Rombunshu (DVD-ROM), 44(1), p.208 - 213, 2022/07
no abstracts in English
Hasegawa, Yuta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Asahi, Yuichi; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 4 Pages, 2022/06
We developed GPU implementation of ensemble data assimilation (DA) using the local ensemble transform Kalman filter (LETKF) with the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM). The performance test was carried out upto 32 ensembles of two-dimensional isotropic turbulence simulations using the D2Q9 LBM. The computational cost of the LETKF was less than or nearly equal to that of the LBM upto eight ensembles, while the former exceeded the latter at larger ensembles. At 32 ensembles, their computational costs per cycle were respectively 28.3 msec and 5.39 msec. These results suggested that further speedup of the LETKF is needed for practical 3D LBM simulations.
Sugihara, Kenta; Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Yamashita, Susumu
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 5 Pages, 2022/06
The phase-field method has been successfully applied to various multi-phase flow problems as an interface tracking method for gas-liquid interfaces. However, the accuracy of the phase-field method depends on hyper-parameters, which are empirically adjusted for each problem. The phase-field method sustains sharp interfaces by the balance between the numerical viscosity of the advection term and the interface modification by the diffusion and anti-diffusion terms. Based on this fact, we propose a method for deriving the optimal hyper-parameters in a non-empirical manner by performing a basic error analysis of the interface advection.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 4 Pages, 2022/06
We have developed a wind simulation code named CityLBM to realize wind digital twins. Mesoscale wind conditions are given as boundary conditions in CityLBM by using a nudging data assimilation method. It is found that conventional approaches with constant nudging coefficients fail to reproduce turbulent intensity in long time simulations, where atmospheric stability conditions change significantly. We propose a dynamic parameter optimization method for the nudging coefficient based on a particle filter. CityLBM was validated against plume dispersion experiments in the complex urban environment of Oklahoma City. The nudging coefficient was updated to reduce the error of the turbulent intensity between the simulation and the observation, and the atmospheric boundary layer was reproduced throughout the day.
Asahi, Yuichi; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Shiba, Hayato*; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 5 Pages, 2022/06
We have ported the GPU accelerated Lattice Boltzmann Method code "CityLBM" to AMD MI100 GPU. We present the performance of CityLBM achieved on NVIDIA P100, V100, A100 GPUs and AMDMI100 GPU. Using the host to host MPI communications, the performance on MI100 GPU is around 20% better than on V100 GPU. It has turned out that most of the kernels are successfully accelerated except for interpolation kernels for Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) method.
Doda, Norihiro; Nakamine, Yoshiaki*; Igawa, Kenichi*; Iwasaki, Takashi*; Murakami, Satoshi*; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 27, 6 Pages, 2022/06
As a part of the development of the "Advanced Reactor Knowledge- and AI-aided Design Integration Approach through the whole plant lifecycle (ARKADIA)" to automatically optimize the life cycle of innovative nuclear reactors including fast reactors, ARKADIA-design is being developed to support the optimization of fast reactor design in the conceptual stage. ARKADIA-Design consists of three systems (Virtual plant Life System (VLS), Evaluation assistance and Application System (EAS), and Knowledge Management System (KMS)). A design optimization framework controls the cooperation between the three systems through the interfaces in each system. This paper reports on the development status of the "VLS interface," which has a control function of coupling analysis codes in VLS.
Ichihara, Yoshitaka*; Nakamura, Naohiro*; Nabeshima, Kunihiko*; Choi, B.; Nishida, Akemi
Kozo Kogaku Rombunshu, B, 68B, p.271 - 283, 2022/04
This paper aims to evaluate the applicability of the equivalent linear analysis method for reinforced concrete, which uses frequency-independent hysteretic damping, to the seismic design of reactor building of the nuclear power plant. To achieve this, we performed three-dimensional FEM analyses of the soil-structure interaction system, focusing on the nonlinear and equivalent linear seismic behavior of a reactor building under an ideal soil condition. From these results, the method of equivalent analysis showed generally good correspondence with the method of the nonlinear analysis, confirming the effectiveness. Moreover, the method tended to lower the structural stiffness compared to the nonlinear analysis model. Therefore, in the evaluation of the maximum shear strain, we consider that the results were more likely to be higher than the results of nonlinear analysis.
Takayama, Yusuke; Kikuchi, Hirohito*
Doboku Gakkai Rombunshu, C (Chiken Kogaku) (Internet), 77(3), p.302 - 313, 2021/09
Numerous swelling pressure tests have been conducted to understand the swelling properties of bentonite which is planned to be used as a buffer material in repositories for the geological disposal of radioactive waste. In this study, in order to clarify the cause of the decrease in swelling pressure during the swell-in pressure test period, the change in wet density distribution inside the specimen during the swelling pressure test was observed by X-ray CT measurement. It was supposed that this phenomenon was caused by the collapse inside the specimen. Furthermore, in order to confirm that collapse is generated by water absorption, the swelling deformation test was carried out under various load conditions. As a result, it was confirmed that collapse occurs even under the load conditions that are equal to or slightly smaller than the swelling pressure. These test data are expected to be used for validation of coupled analysis codes for evaluating the mechanical behavior of disposal facilities during re-saturation period.
Oba, Kyoko
Kogaku Kyoiku, 69(5), p.95 - 98, 2021/09
This paper introduces the recent topics of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan Ethics Committee. In addition, referring to the topics, the abilities and sensibilities that engineers should have in the future will be described.
Hasegawa, Yuta; Aoki, Takayuki*; Kobayashi, Hiromichi*; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Onodera, Naoyuki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 6 Pages, 2021/05
We introduce an improved domain partitioning method called "tree cutting approach" for the aerodynamics simulation code based on the lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) with the forest-of-octrees-based local mesh refinement (LMR). The conventional domain partitioning algorithm based on the space-filling curve (SFC), which is widely used in LMR, caused a costly halo data communication which became a bottleneck of our aerodynamics simulation on the GPU-based supercomputers. Our tree cutting approach adopts a hybrid domain partitioning with the coarse structured block decomposition and the SFC partitioning in each block. This hybrid approach improved the locality and the topology of the partitioned sub-domains and reduced the amount of the halo communication to one-third of the original SFC approach. The code achieved 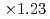 speedup on 8 GPUs, and achieved
speedup on 8 GPUs, and achieved 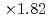 speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega-lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs with strong scaling test.
speedup at the performance of 2207 MLUPS (mega-lattice update per second) on 128 GPUs with strong scaling test.
Matsushita, Kentaro; Fujisaki, Tatsuya*; Ezure, Toshiki; Tanaka, Masaaki; Uchida, Mao*; Sakai, Takaaki*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 6 Pages, 2021/05
For the gas entrainment vortex at the free surface in sodium-cooled fast reactors, development of the numerical analysis method to evaluate amount of the gas entrainment from the free surface has been developing. In this paper, the automatic creation of analysis meshes which can suppress the calculation cost while maintaining the prediction accuracy of the vortex shape is investigated, and the adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) method is examined to the creation of analysis mesh applying to the unsteady vortex system. The refined mesh based on the criterion evaluated by vorticity, Q-value as second invariant of the velocity and the discriminant for the eigen equation of the velocity gradient tensor is considered, and it found that the AMR method based on Q-value can refine the analysis meshes most efficiently.
Doda, Norihiro; Uwaba, Tomoyuki; Nemoto, Toshiyuki*; Yokoyama, Kenji; Tanaka, Masaaki
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 4 Pages, 2021/05
For design optimization of fast reactors, in order to consider the feedback reactivity due to thermal deformation of the core when the core temperature rises, which could not be considered in the conventional design analysis, a neutronics, thermal-hydraulics, and structure mechanics coupled analysis method has been developed. Neutronics code, plant dynamics code, and structural mechanics code are coupled by a control module in python script. This paper outlines the coupling method of analysis codes and the results of its application to an experiment in an actual plant.
Onodera, Naoyuki; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Hasegawa, Yuta; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Aoki, Takayuki*
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 3 Pages, 2021/05
We develop a mixed-precision preconditioner for the pressure Poisson equation in a two-phase flow CFD code JUPITER-AMR. The multi-grid (MG) preconditioner is constructed based on the geometric MG method with a three- stage V-cycle, and a cache-reuse SOR (CR-SOR) method at each stage. The numerical experiments are conducted for two-phase flows in a fuel bundle of a nuclear reactor. The MG-CG solver in single-precision shows the same convergence histories as double-precision, which is about 75% of the computational time in double-precision. In the strong scaling test, the MG-CG solver in single-precision is accelerated by 1.88 times between 32 and 96 GPUs.
Asahi, Yuichi; Hatayama, Sora*; Shimokawabe, Takashi*; Onodera, Naoyuki; Hasegawa, Yuta; Idomura, Yasuhiro
Keisan Kogaku Koenkai Rombunshu (CD-ROM), 26, 4 Pages, 2021/05
We develop a convolutional neural network model to predict the multi-resolution steady flow. Based on the state-of-the-art image-to-image translation model Pix2PixHD, our model can predict the high resolution flow field from the signed distance function. By patching the high resolution data, the memory requirements in our model is suppressed compared to Pix2PixHD.
Oba, Kyoko; Yoshizawa, Atsufumi*; Kitamura, Masaharu*
Kogaku Kyoiku, 69(3), p.3 - 10, 2021/05
The purpose of engineering ethics education is to understand the effects and impacts of technology on society and nature and the responsibilities that engineers have to fulfill for society. There are many cases used in the educational method so that the students can understand the problems surrounding the engineers. However, most of the cases correspond to event scenarios where engineers have failed to maintain safety. Resilience engineering was born from the criticism of safety measures for the purpose of preventing recurrence by seeking human error and organizational culture as the cause of accidents in the field of ergonomics. Its features are that people are considered as beings that realize safety in dangerous systems, and that they focus on good practices. This paper describes the improvement of engineering ethics education by utilizing resilience engineering concept.